Diabetes
There is an urgency for greater action to improve diabetes outcomes and reduce the global burden of diabetes now affecting more than 425 million people, of which one-third are people older than 65 years. The estimates of children and adolescents below age 20 with type 1 diabetes has risen to over a million
. If nothing is done, the number of people with diabetes may rise to 629 million in 2045, although positively the incidence has started to drop in some high income countries. At the same time, a further 352 million people with impaired glucose tolerance are at high risk of developing diabetes.
Read more about the prevalence of diabetes
http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas
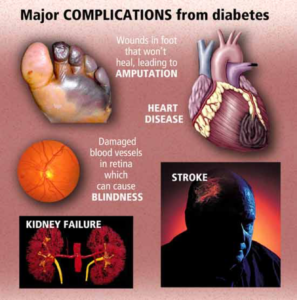
Diabetes can affect many major organs in your body, which can lead to an array of serious complications when left untreated. So , the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications These medical problems include:
1- Cardiovascular disease
Diabetes is a risk for atherosclerosis (hardening of the walls and narrowing of arteries) which may predispose to various cardiovascular problems including ischemic heart disease (angina, heart attack), stroke, peripheral arterial disease and limb gangrene and amputation.
2- Kidney disease (Nephropathy)
Longstanding and uncontrolled diabetes can lead to irreversible end-stage kidney disease(kidney failure) , which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
3- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Diabetes leads to damage of the walls of the tiny blood vessels of the nerves of the limbs especially the legs. This can cause tingling, numbness, burning sensation that usually begins at the tips of the toes or fingers and gradually spreads upward. If left untreated, it will lead to loss of all sensation which could be a risk factor for foot ulcers and amputation. Nerves of the digestive system could be affected leading to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Also nerve damage can lead to erectile dysfunction in men.
4- Eye damage (retinopathy)
Diabetes can injure the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), potentially leading to blindness. It also increases the risk of other serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
5- Skin and mouth conditions
Diabetes is a risk for bacterial and fungal skin infections as well as other skin disorders. Poor dental hygiene is a risk factor for mouth infections.


